Automated Design of Protein-binding Riboswitches for Sensing Human Biomarkers in a Cell-free Expression System
ID# 2022-5522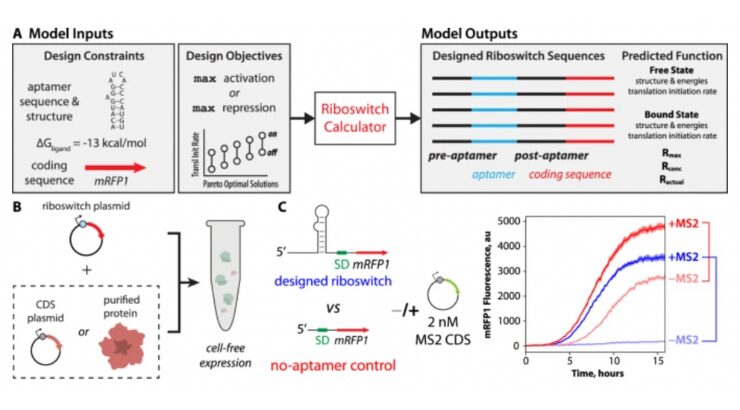
Technology Summary
The inventors developed an integrated computational & experimental platform to convert protein-binding RNA aptamers into riboswitch cell-free biosensors. The inventors demonstrated the platform by developing protein-sensing riboswitches for human monomeric C-reactive protein and human interleukin-32γ, which are biomarkers for heart disease, viral infection and inflammation, as well as phage MS2 coat protein. The riboswitch sensors regulated output protein expression levels by up to 21-fold with protein concentrations within the human serum physiological range. The inventors have identified over 20 protein biomarkers that could be detected by engineering riboswitch cell-free biosensors and have designed devices that utilize riboswitch cell-free biosensors for use in medical diagnostics. A more detailed description can be found in the inventor’s peer-reviewed April 27, 2023 Nature Communication eponymous publication entitled “Automated Design of Protein-binding Riboswitches for Sensing Human Biomarkers in a Cell-free Expression System.”
Application & Market Utility
The inventors foresee commercial utility in developing this platform technology for low-cost medical diagnostics for human proteins found in serum, saliva, or other fluids. The inventors believe that the reagent cost of an assay having long shelf-life at room temperature may be around one dollar ($1).
Next Steps
The inventors foresee commercial utility in developing this platform technology.

